Ever spend hours swapping MOSFETs only to have your circuit still misbehave? Overheating, mysterious ringing, and unexpected shutdowns—sounds familiar? For years, I blamed the MOSFET itself, assuming newer or “better” parts would fix everything.
Here’s the twist: the MOSFET is just the actor. The real director is the gate driver, silently orchestrating every switch, transition, and joule of energy. Without a competent driver, even the most advanced MOSFET stumbles—switching losses spike, EMI skyrockets, thermal stress mounts, and lifetime plummets.
In this Hackaday.io post, I’ll break down practical techniques, PCB layout insights, driver design tips, and field-tested solutions—all actionable, deep, and perfect for makers, hobbyists, and professional engineers alike.
The MOSFET and Its Gate Driver — The Actor and the Director
Imagine a MOSFET switching at hundreds of kHz, handling amps of current. It’s brilliant when guided well. But slow gate voltage, insufficient drive current, or a sloppy PCB layout? Performance collapses. You see high transition losses, EMI spikes, ringing, and heat buildup.
Takeaway: Designing a MOSFET driver isn’t optional—it’s designing reliability.
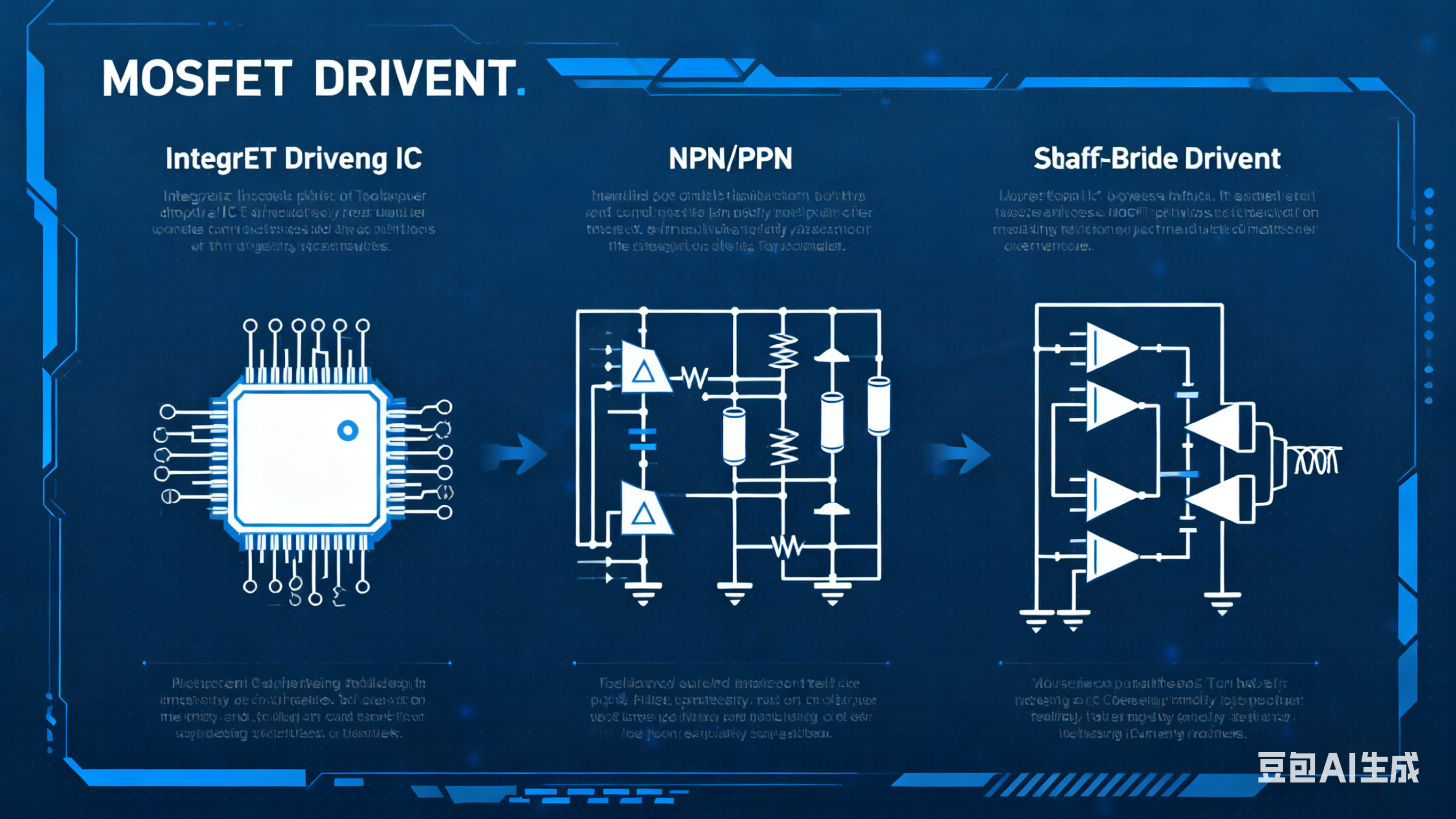
Driver Topologies That Matter
-
Integrated driver ICs — simple, reliable for standard modules.
-
Push-pull (totem-pole) drivers — provide sharp edges for fast switching.
-
Half-bridge drivers — essential for paired MOSFETs in motor drives and DC-DC converters.
-
Turn-off acceleration pulses — speed turn-off, but risky if misused.
6 Questions Every Hardware Hacker Must Ask
-
Is the drive current sufficient?
Slow gate charging = longer transitions = higher switching losses. Boost carefully. -
Is the gate voltage correct?
Too high = stress; too low = incomplete conduction. -
Output impedance balanced?
Low impedance stabilizes voltage; small series resistors can tune speed and reduce ringing. -
PCB layout optimized?
Switching loop area dictates EMI and ringing. Short traces, clear returns, solid ground planes. -
Thermal paths adequate?
Even the best driver fails without proper heat management. -
Damping elements in place?
Gate resistors, snubbers, and targeted damping often solve stubborn field problems.
Practical Tips You Can Apply Today
-
Use small series gate resistors to control ringing.
-
Add snubbers at high di/dt nodes.
-
Place decoupling capacitors close to switching devices.
-
Combine low-impedance drivers with small resistors for balanced performance.
-
Add thermal sensors or protection for live circuits.
Troubleshooting Workflow
-
Capture gate waveforms: rise/fall times, overshoot.
-
Verify gate resistor values and driver current capability.
-
Measure switch-node spikes to infer loop inductance.
-
Temporarily slow switching (increase gate resistance) — improvement points to parasitic issues.
-
Add damping or snubbers and reassess.
Busting Common Myths
-
“New MOSFET fixes everything.” → False. Driver design matters more.
-
“Max gate voltage is best.” → False. Overvoltage shortens life.
-
“Rds(on) tells the whole story.” → False. Dynamic parameters (Coss, Ciss, Qg) dominate switching behavior.
Final Thoughts for Hackers and Makers
Stop swapping MOSFETs blindly. Focus on gate driver optimization, PCB layout, thermal design, and damping strategies. Often, simple tweaks solve the hardest field problems—faster, cheaper, and more reliably.
💬 Share your waveforms, operating voltage/frequency, and load type, and I’ll guide you through a practical diagnostic roadmap for circuits, layout, and tuning—without recommending specific products.
SEO/Discoverability Keywords (Hackaday.io Friendly)
MOSFET troubleshooting, gate driver design, switching losses, EMI reduction, PCB layout tips, thermal management MOSFET, power electronics hacking, DC-DC converter design, motor driver circuits, MOSFET ringing issues
 MOSFET
MOSFET
Discussions
Become a Hackaday.io Member
Create an account to leave a comment. Already have an account? Log In.