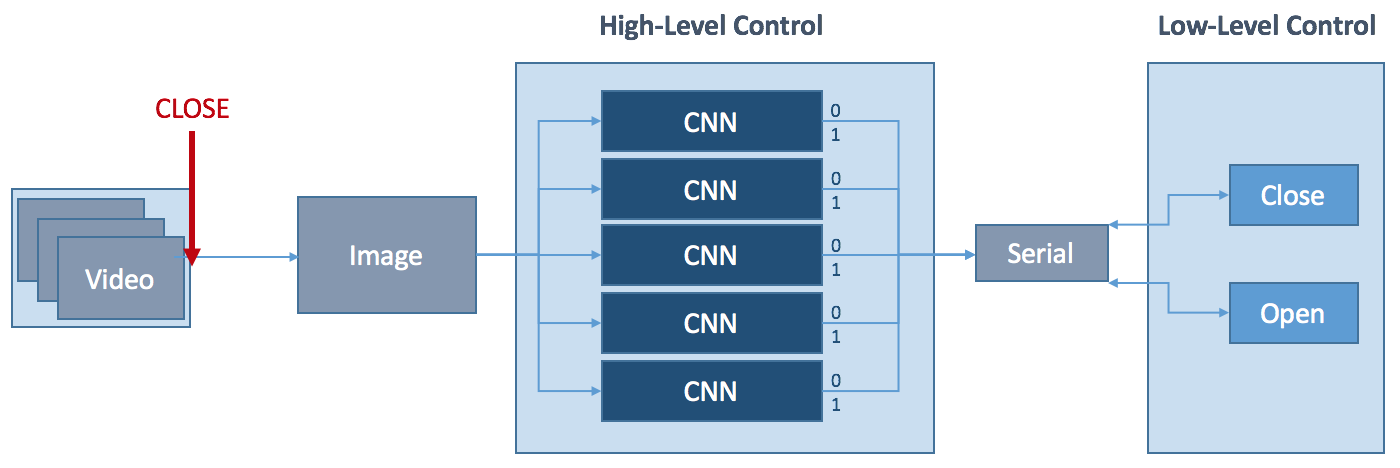
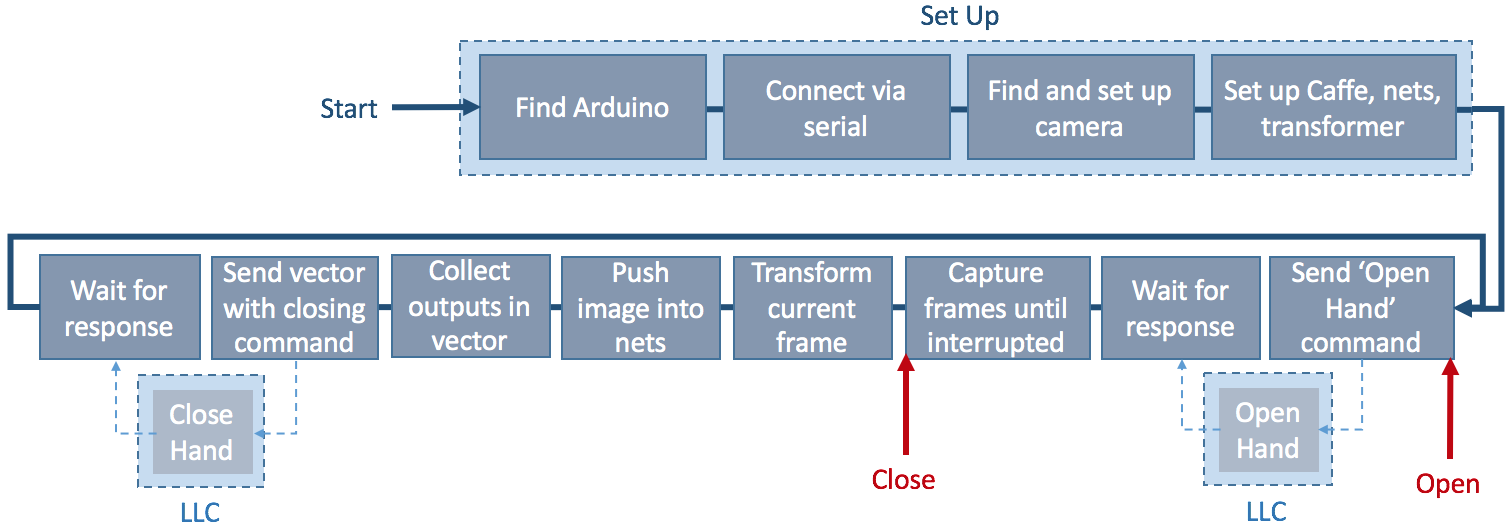
I started this project as a final year EE student because I was curious about exploring the fields of Artificial Intelligence, Deep Learning and Machine Learning in general, as well as improve my electronics and CAD skills. But I wanted to create something that would one day be able to help people. This is how I became interested in creating a robotic hand that ultimately can be used as a prosthetic, but will also be suitable for more general automatic robotic grasping tasks. Given a very limited budget I decided to explore how far I can push functionality and intelligence of the hand with minimal sensory input. This is what led me to developing a hardware and software system that can make its own grasping choices based solemnly on visual input provided by webcam. The functionality of the hand is as follows in a nutshell:
- point the hand at any object,
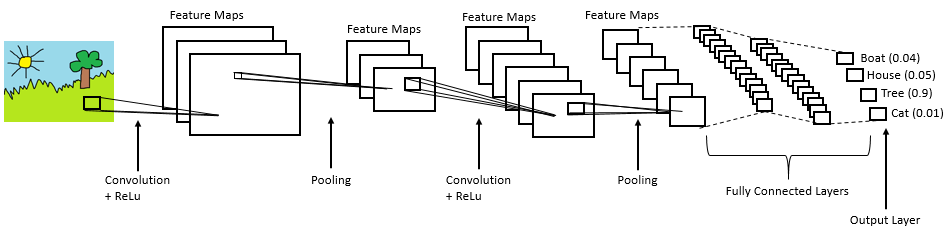
- artificial intelligence via Convolutional Neural Networks decides the best way to grasp it,
- prosthetic hand grips the object as instructed by the neural nets.
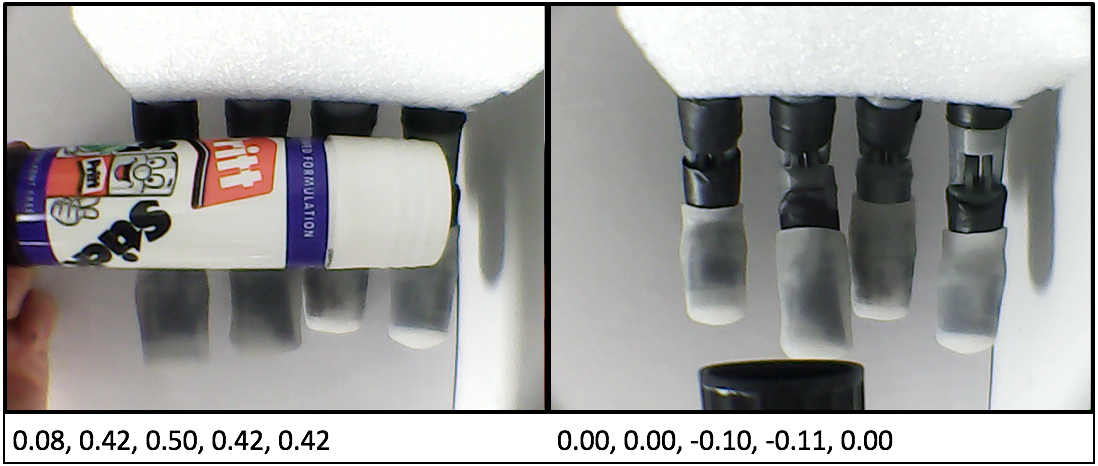
The results so far have been incredibly promising as can be seen in the video below.
Licenses:
http://opencv.org/license.html
 Stephanie Stoll
Stephanie Stoll



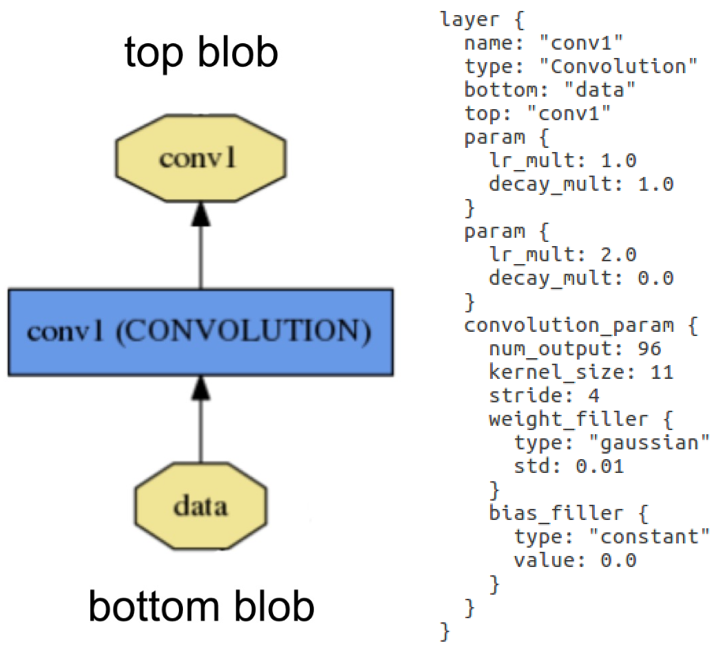 Layer example: Layer "conv1" takes in data through bottom connection and outputs conv1 through top connection. Parameters for convolution operation are defined in the net's prototxt file and can be visualised as a DAG (directed acyclic graph).
Layer example: Layer "conv1" takes in data through bottom connection and outputs conv1 through top connection. Parameters for convolution operation are defined in the net's prototxt file and can be visualised as a DAG (directed acyclic graph).
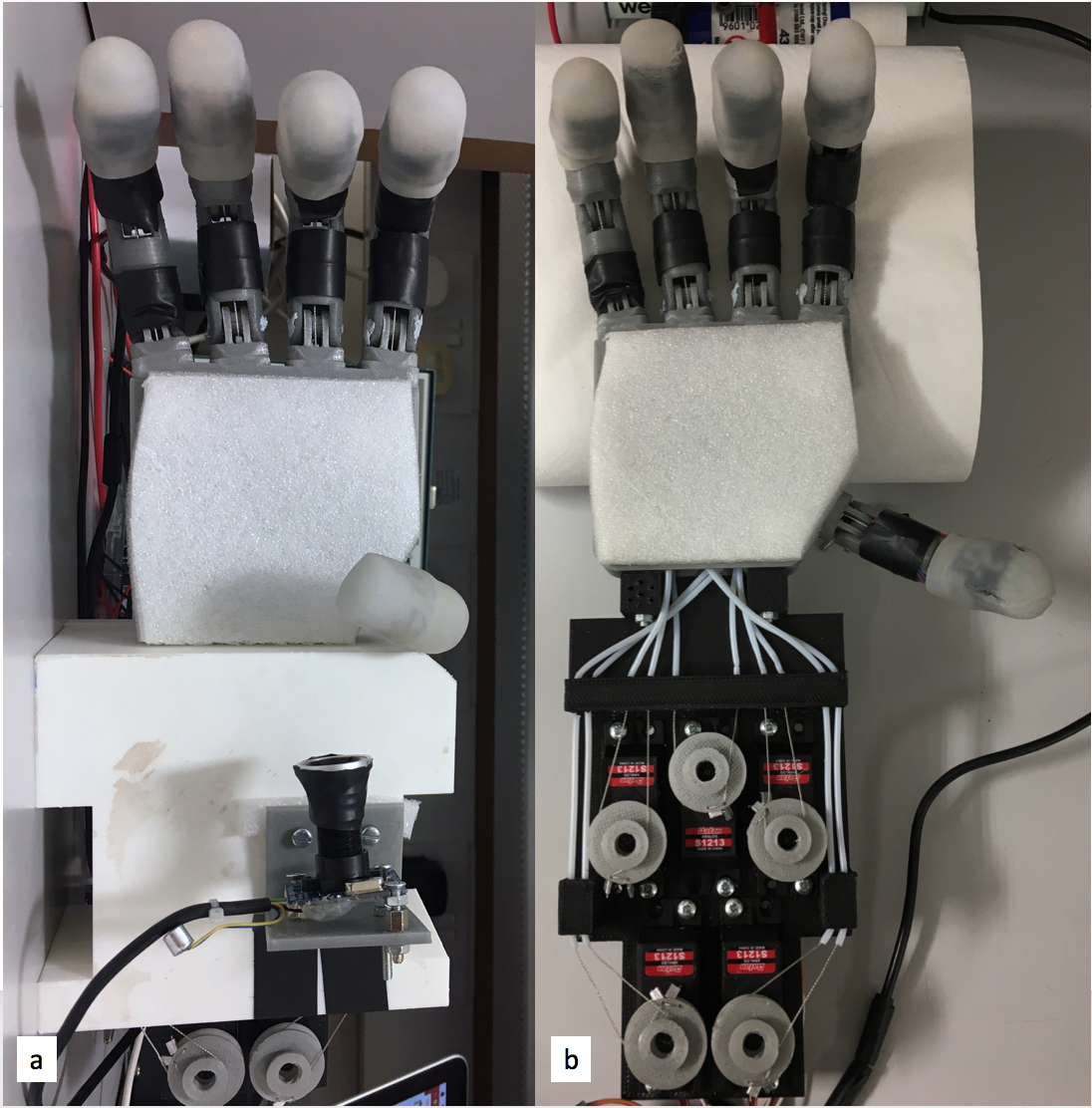
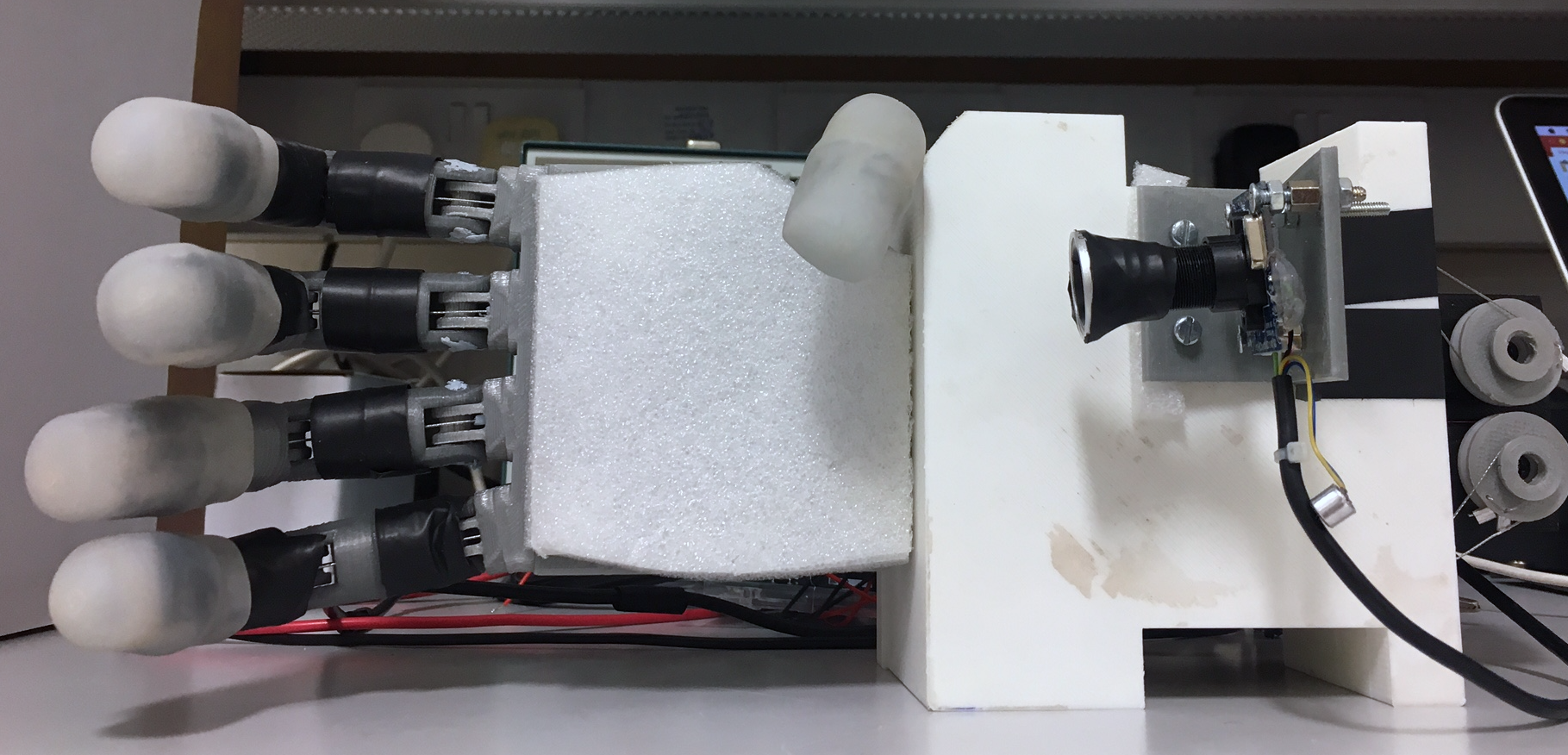
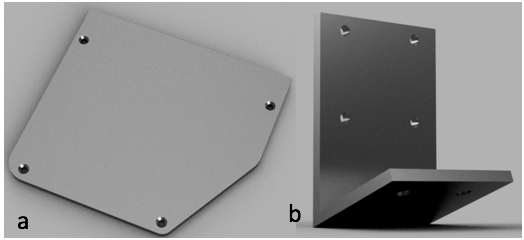
 The fully assembled hand prototype with mounted camera and servo bed cover(a), the hand prototype with servo bed cover and camera removed to give view to the actuator and tendon system (b).
The fully assembled hand prototype with mounted camera and servo bed cover(a), the hand prototype with servo bed cover and camera removed to give view to the actuator and tendon system (b).
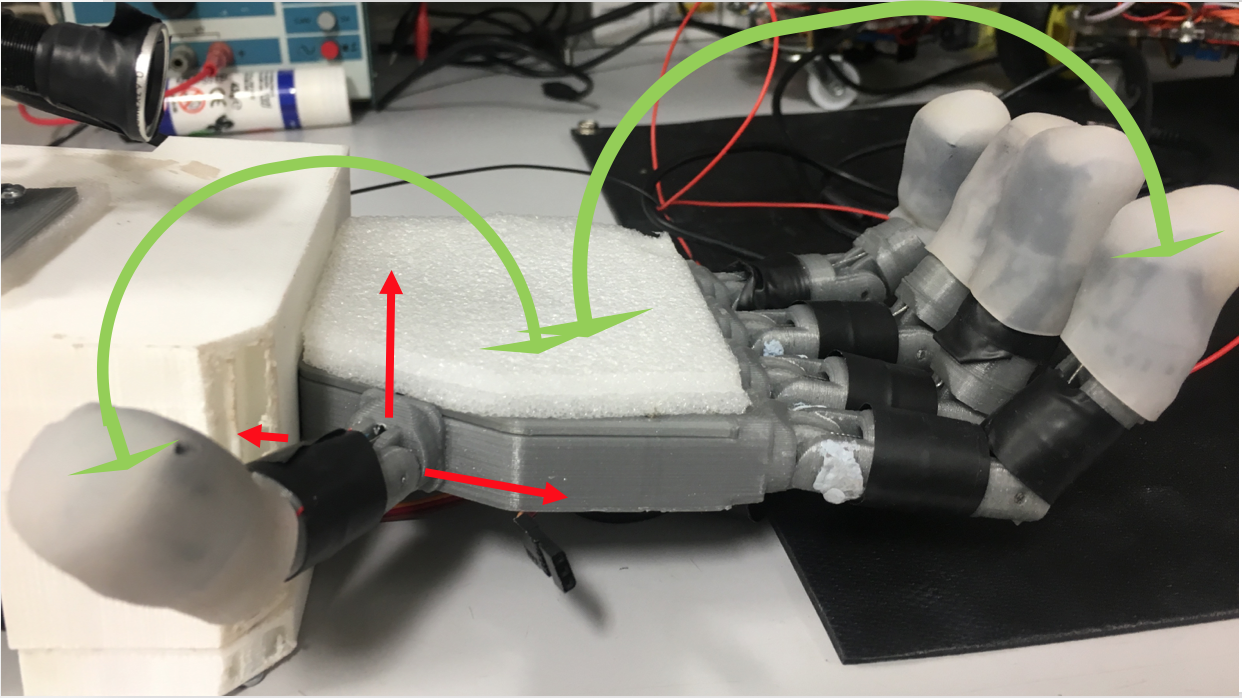 All fingers are able of flexion and extension (indicated by green arrows for thumb and index), but not of abduction, adduction, neither radial nor palmar (indicated for the thumb in red).
All fingers are able of flexion and extension (indicated by green arrows for thumb and index), but not of abduction, adduction, neither radial nor palmar (indicated for the thumb in red).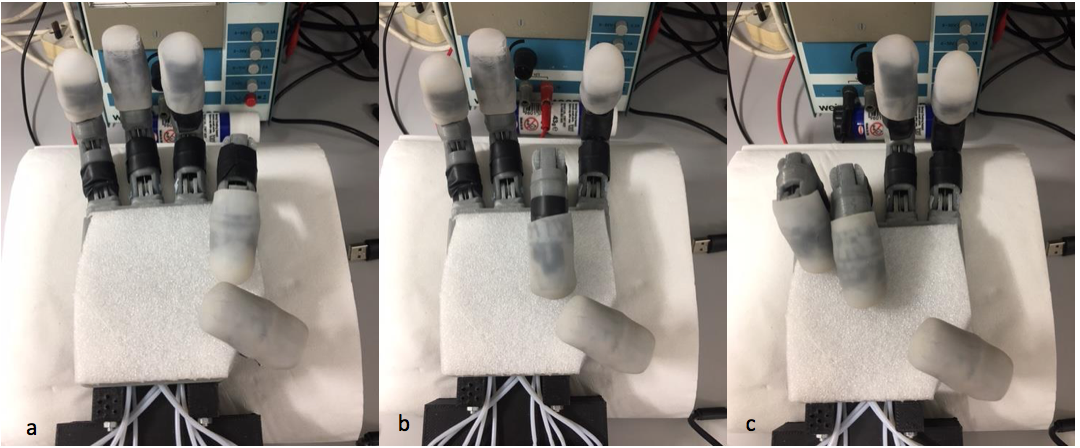 The opposability of the thumb is limited to being able to perform pinch grasps with the index (a) and the middle finger (b), but not with the ring or little finger (c).
The opposability of the thumb is limited to being able to perform pinch grasps with the index (a) and the middle finger (b), but not with the ring or little finger (c).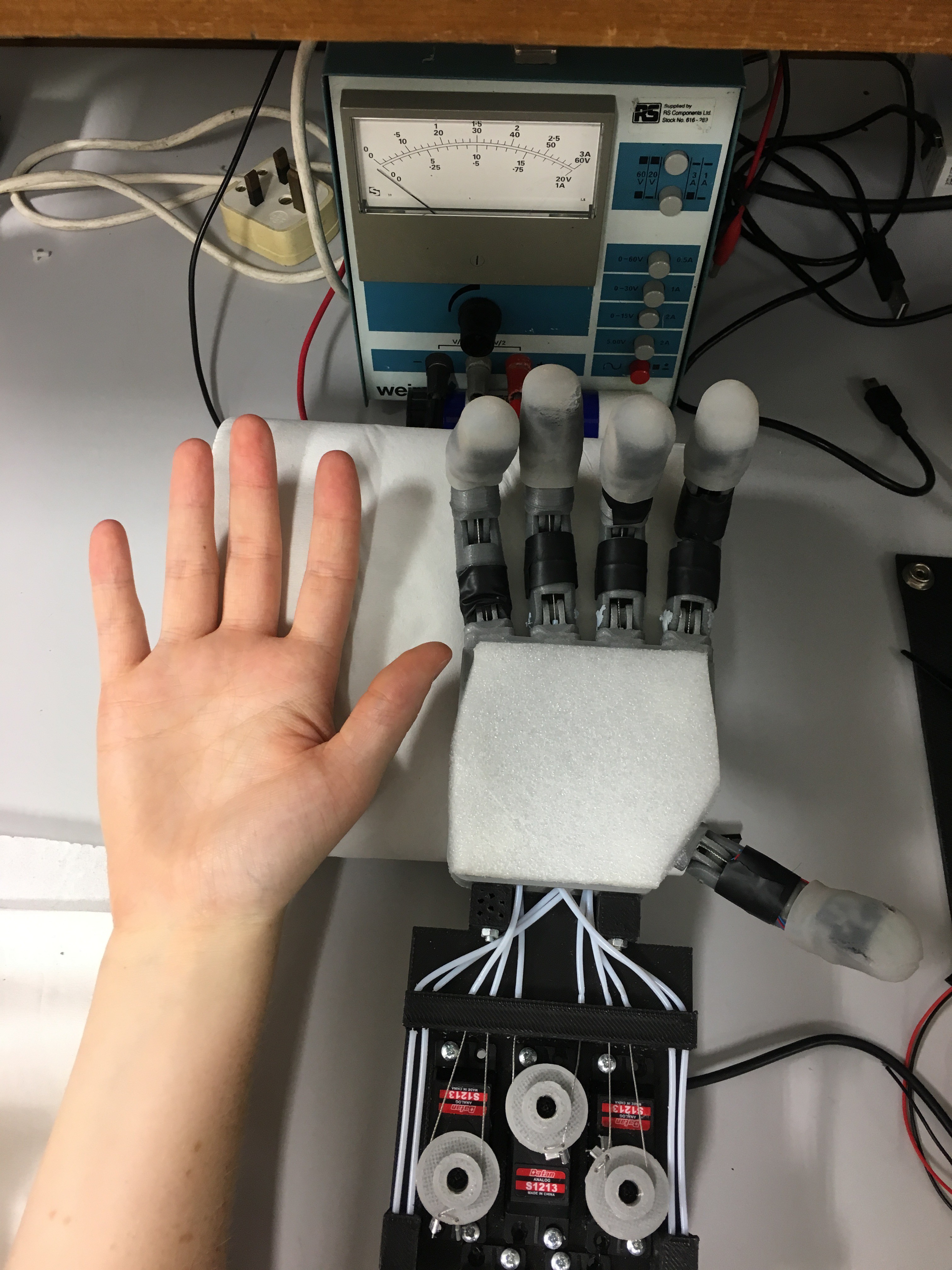
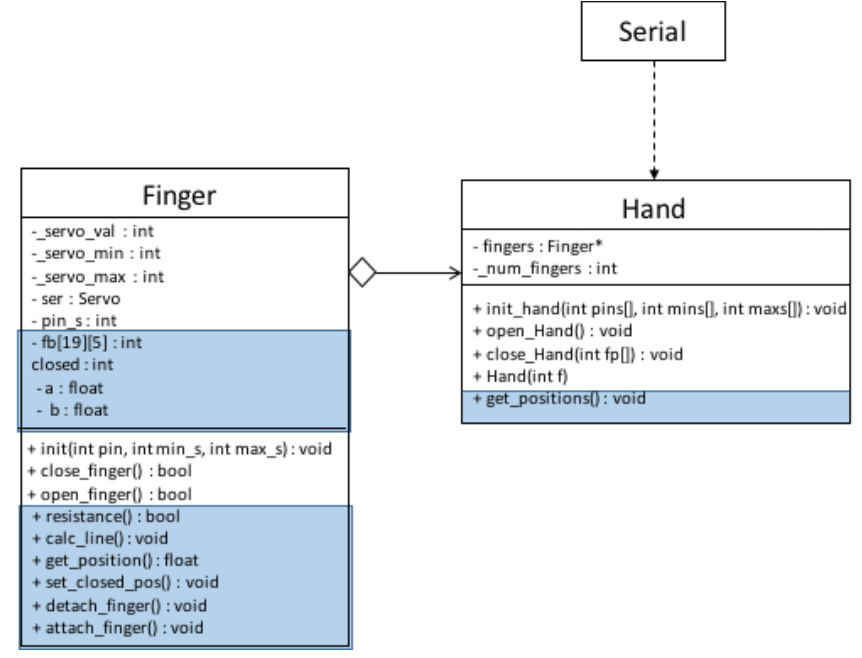 UML diagram of low-level API. Parts of the extended API used to collect training data are marked in blue.
UML diagram of low-level API. Parts of the extended API used to collect training data are marked in blue.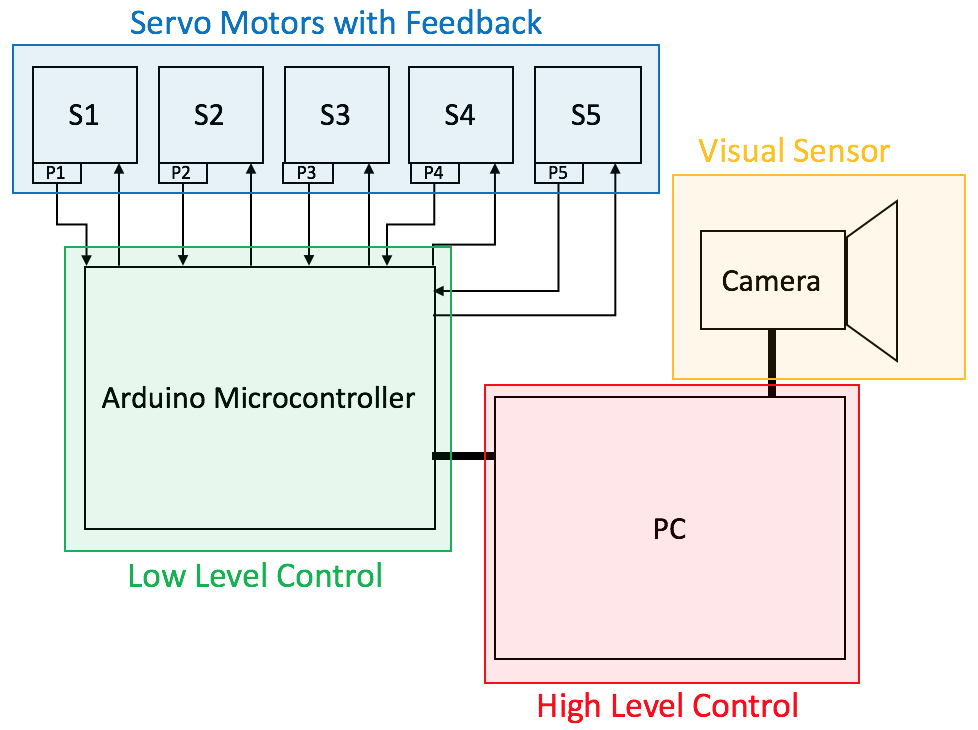
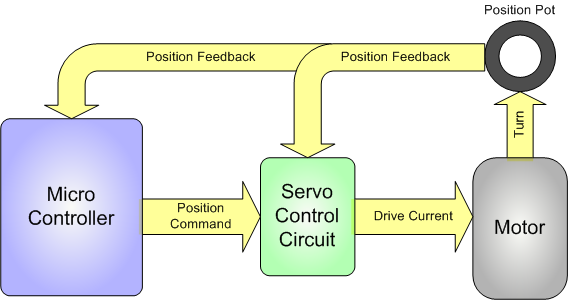 Analog feedback servo motor feeding the potentiometer information from the motor shaft to the microcontroller
Analog feedback servo motor feeding the potentiometer information from the motor shaft to the microcontroller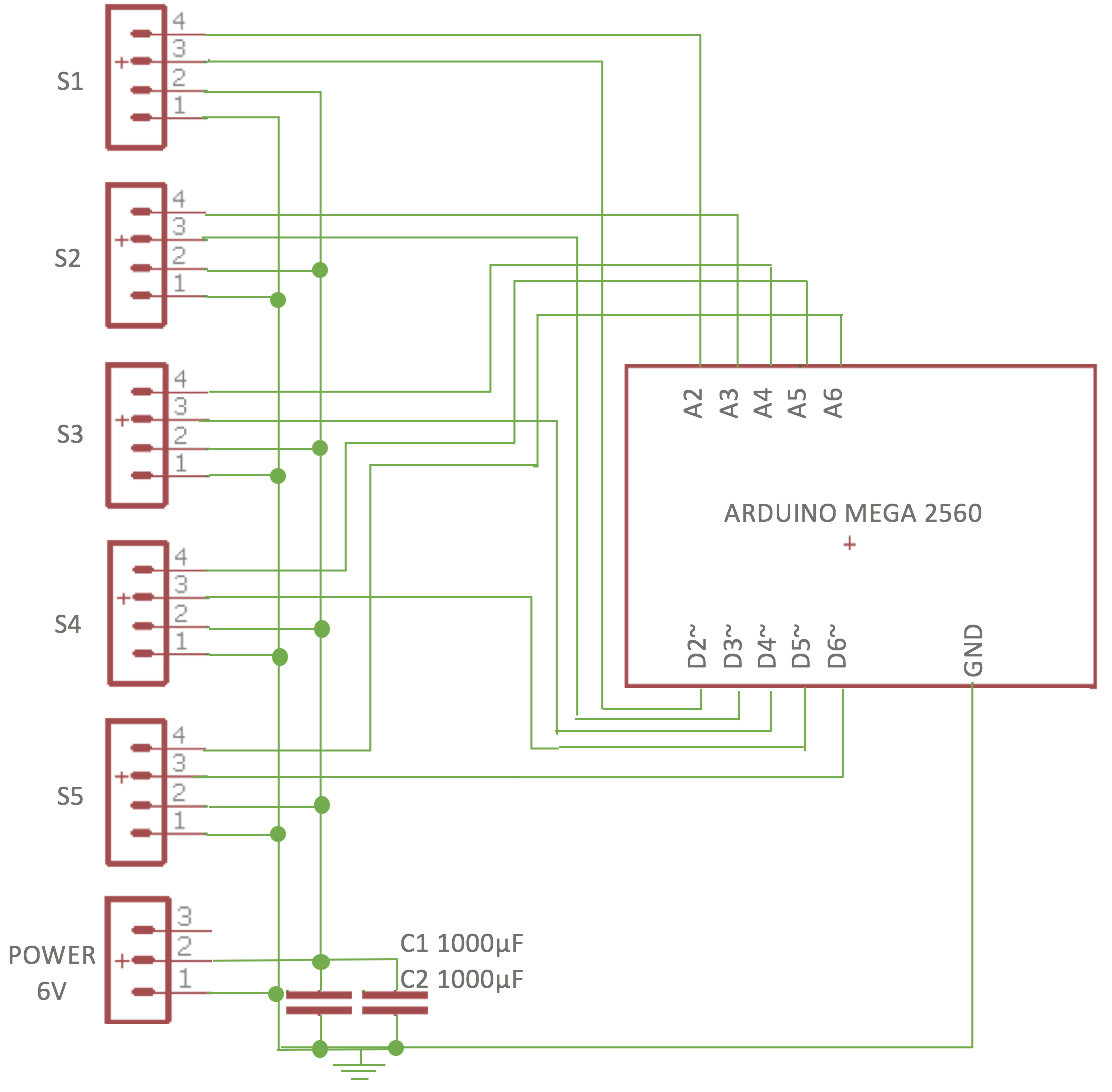

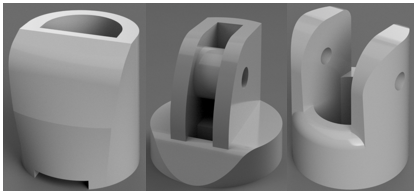 finger tip (left), male phalanx base part (middle) and female phalanx base part (right).
finger tip (left), male phalanx base part (middle) and female phalanx base part (right).
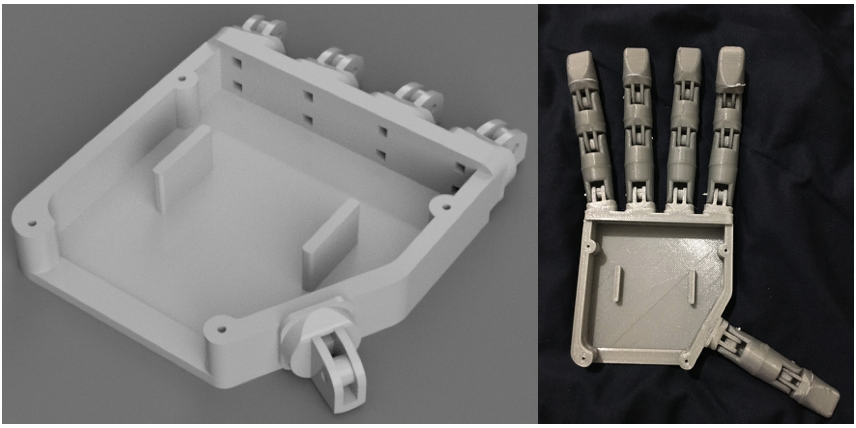
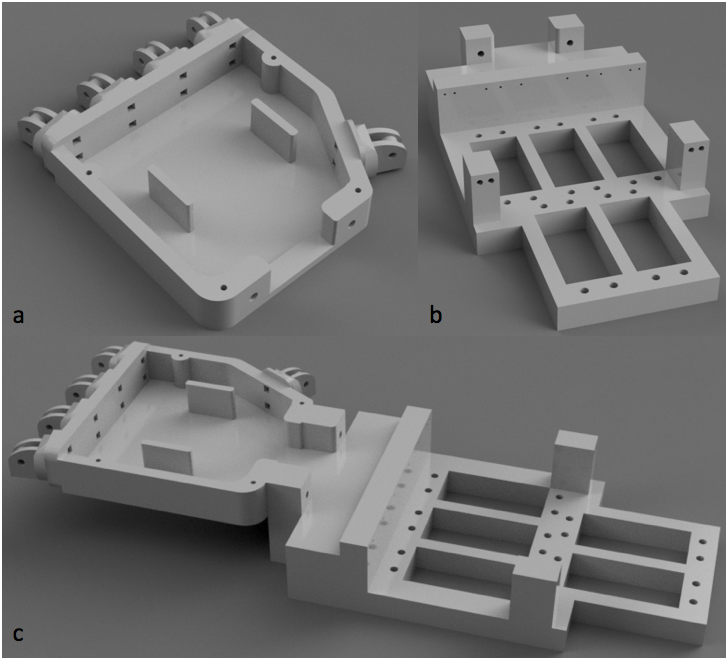
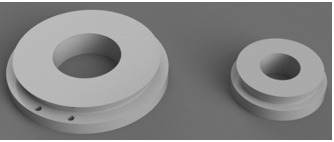
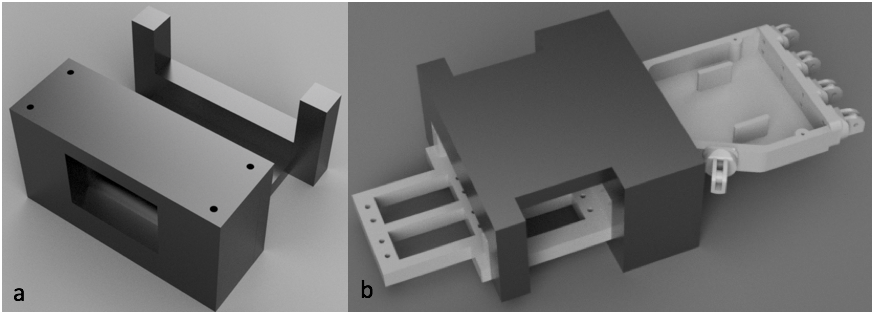
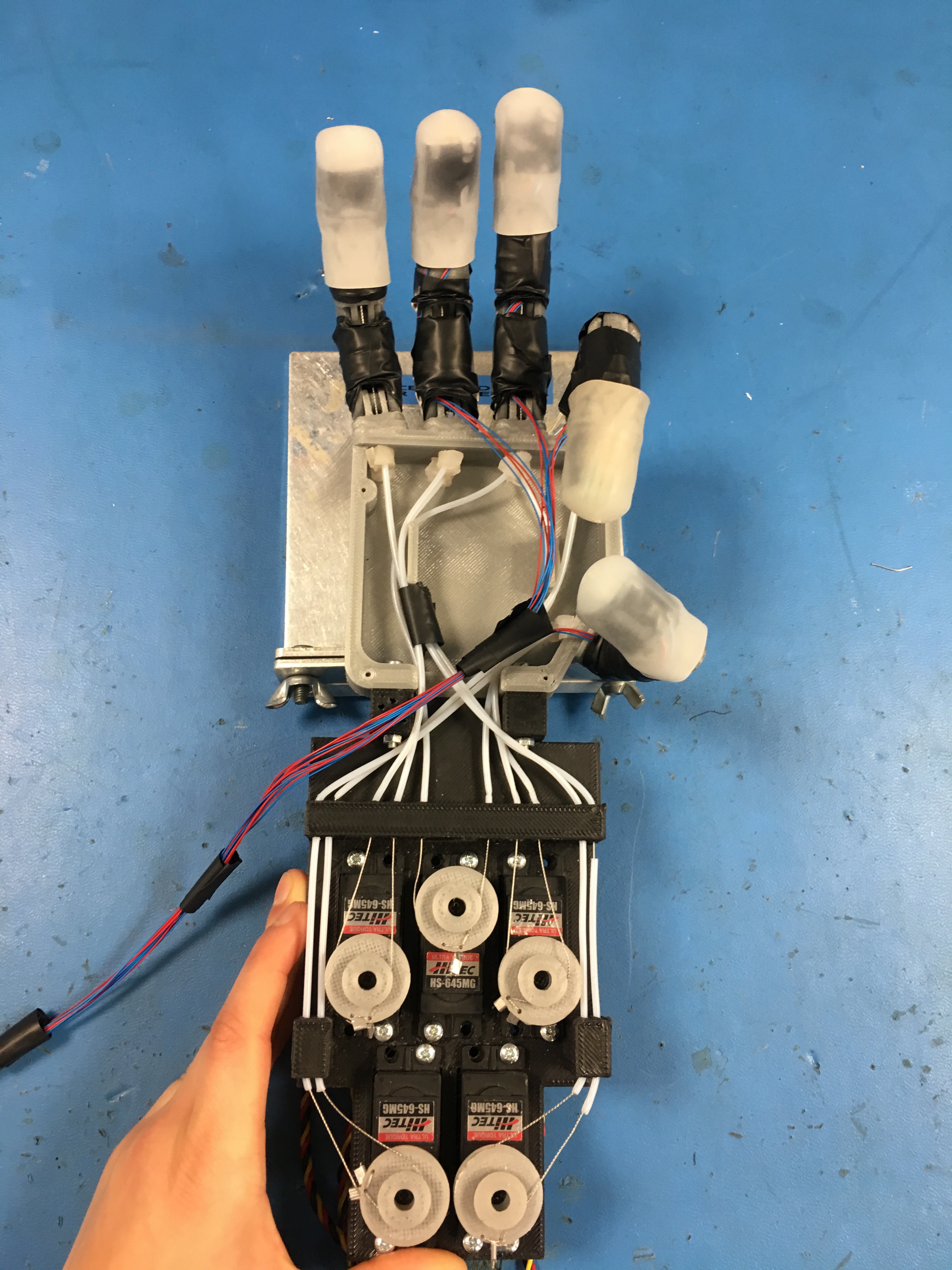 This shows the full positioning of the servos, as well as the whole Bowden system (ignore the cables, they were for some force sensors I tried).
This shows the full positioning of the servos, as well as the whole Bowden system (ignore the cables, they were for some force sensors I tried).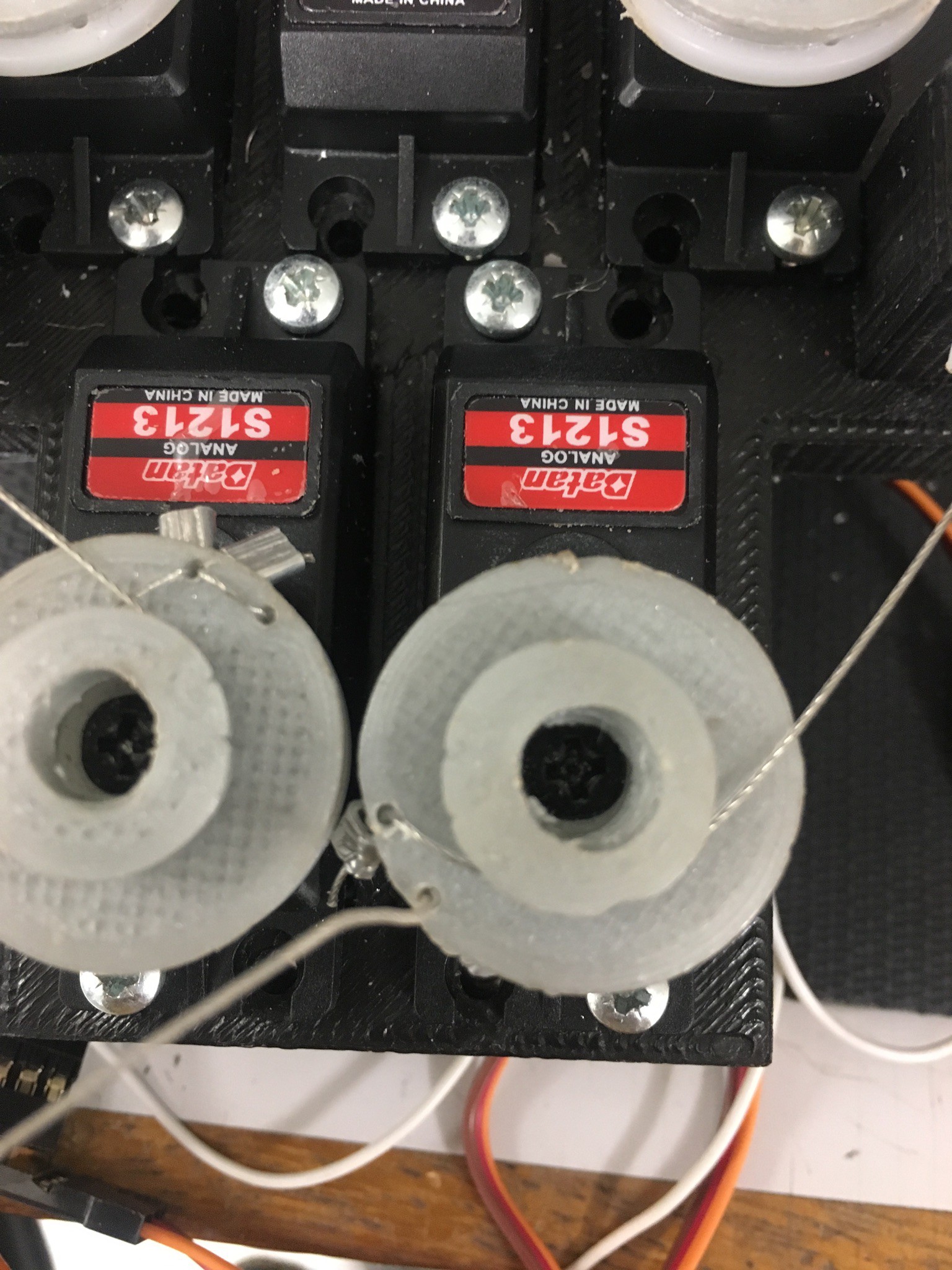

 Alvaro Villoslada
Alvaro Villoslada
 New Dexterity
New Dexterity
 RaptorTech
RaptorTech
 Debargha Ganguly
Debargha Ganguly